Atılgan S.B., Sargın B., Usta F.D. (2014). “Measuring Job Satisfaction in Organization Case Study: Atilgan Automotive Inc.”
INTRODUCTION
Job satisfaction is a very important concept to understand. Its factors should be understood and developed according to employees’ wishes. By this way, as an individual employee would be happier, less stressful; additionally, as a company, more satisfied employees mean more efficient and productive working. As a result, more satisfaction brings benefits to both sides. However, satisfaction is not something to understand easily, it is not concrete, but there are some methods to measure it. In this essay, we try to explain firstly what job satisfaction is, what factors have an impact on job satisfaction and how we can measure it. The second part of the essay involves the case study on Atılgan Automotive Inc.
A. LITERATURE REVIEW
- Definition of Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction can be defined in many different ways. Some people claim that it is basically how content an individual is with his or her job. On the other hand, others believe it is not as simplistic as this definition suggests and instead that multidimensional psychological responses to one’s job are involved. Researchers have also noted that job satisfaction measures vary in the extent to which they measure feelings about the job effective job satisfaction. Locke and Lathan, two important scholars, explain a comprehensive definition of job satisfaction that is pleasurable or positive emotional state resulting from the appraisal of one’s job. According to Mitchell and Lasan, it is generally recognized in the organizational behavior field that job satisfaction is the most important and frequently studied attitude.
Also, Luthan explains that there are three crucial dimensions for job satisfaction: ‘‘First of all, job satisfaction is an emotional response to a job situation. As such it cannot be seen, it can only be inferred. Secondly, job satisfaction is often determined by how well the outcome meets or exceed expectations. For instance, if organization participants feel that they are working much harder than others in the department but are receiving fewer rewards they will probably have negative attitudes towards the work, the boss and or coworkers. On the other hand, if they feel they are being treated very well and are being paid equitably, they are likely to have positive attitudes towards the job. Lastly, job satisfaction represents several related attitudes which are most important characteristics of a job about which people have an effective response and these are: the work itself, pay, promotion opportunities, supervision, and coworkers.’’
- Importance of Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction is frequently studied issue by several disciplines, such as economics, psychology, sociology etc. Diaz-Serrano and Cabral Vieira explain its reason by believing in that job satisfaction affect labor and market behavior and influence work productivity, work effort, employee absenteeism, and staff turnover. Therefore job satisfaction is important for an organization. High job satisfaction has lots of benefits for the organization. For example, increases commitment to the organization, productivity, creativity etc. As a result of all those effects, profit will also increase in the organization.
Job dissatisfaction has lots of negative effects on the company. According to Freeman, The success of any company is directly link to the satisfaction of the employees who embody that company, that retaining talented people is critical to the success of any organization. Low job satisfaction increases turnover, absenteeism, tardiness, accidents, strikes, grievances, sabotage etc. Briefly, job dissatisfaction will lead to carelessness and unlikeableness to the job and result of those factors is losing prestige, financial problems, and low productivity. To sum up, measuring job satisfaction in an organization help managers to understand how they can improve their conditions, needs of employees, and in which ways productivity can be increased.
- The Affective Factors of Job Satisfaction
Through a review of the literature, we can classify the variables in mainly two broad categories: Organizational factors and personal factors. The organization determinants of employee satisfaction play a very important role. The employees spend a major part of their time in an organization so there is the number of organizational variables that determine employee satisfaction of the employees. Employee satisfaction in the organization can be increased by organizing and managing these organizational variables or organizational factors. These factors are organization development, job security, working hours, career opportunities, and relationship with supervisor, workgroup etc. If all these factors are not good enough, employees will be stressful and their stress will reflect their job performance in a negative way, so organizational factors are important to keep job satisfaction at a high level.
Personal factors are the second important group of factors. The personal determinants also help a lot in maintaining the motivation and personal factors of the employees to work effectively and efficiently. Employee satisfaction can be related to psychological factors and so numbers of personal variables determine the employee satisfaction of the employees. Personality, age, gender, education, and expectation are basic personal factors. In addition, expectation one of the most important one because; higher expectation brings higher job dissatisfaction.
- Measuring Methods
The majority of job satisfaction basically divided two which are self-reports and based on multi-item scales. There are several measures that developed over the years; however, they vary in terms of how carefully and distinctively they are conceptualized with respect to effective.
- Self-reports
A self-report study is a type of survey, questionnaire which respondents read the question and select a response by themselves without researcher interference. A self-report is any method which involves asking a participant about their feelings, attitudes, and beliefs about a job. Examples can be questionnaires and interviews for self-reports.
- Multi-item Scales:
One of the major job satisfaction measurement is a multi-item scale. It is the most common way to measure job satisfaction. There are many to measure job satisfaction but the Job Descriptive Index and Minnesota are widely used. In the below, I will explain the methods and in the case study, the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire is used to measure job satisfaction in the company.
The Job Descriptive Index
The Job Descriptive Index measures one’s satisfaction in five stages: pay, promotions and promotion opportunities, coworkers, supervision, and the work itself. The scale is simple, participants answer either yes, no, or can’t decide in response to whether given statements accurately describe one’s job.
The Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire
The Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire is designed to measure an employee’s satisfaction with his or her job. The Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire measures job satisfaction in 20 facets and has a long form with 100 questions and a short form with 20 questions. Also, it is a rating scale for assessing job satisfaction in which people indicate the extent to which they are satisfied with various aspects of their jobs. For example, 1 represents one is fully dissatisfied from his/her job, on the other hand, 5 represents one is fully satisfied from his/her job.
B. CASE STUDY
After doing the literature review, we chose a company to apply what we learned from the literature review, and also to see the application of this theoretical knowledge on it. We chose Atılgan Automotive Inc. In this part, how we prepare the questionnaire, how we applied it and what was the result will be explained
- Company Profile
Atılgan Automotive is a part of the Atılgan Group. In 1969, Atılgan Automotive was established in Rize by Ahmet Atılgan. Then, in Istanbul Aksaray, spare parts wholesale organization was formed. In 1996 Rize Atılgan Ford Dealership; in 2002 Artvin Atılgan Ford Dealership were established. And finally, Istanbul Atılgan Ford Dealership was established in 2007. By this time, management has handed over from Ahmet Atılgan to his four sons.
Now, Atılgan Group includes ATY Automotive, which sells the ancillary industries’ spare parts; Atıl-san Automotive, which manufactures spare parts for key-industry and sub-industry; Kackar Hotel; Kackar Insurance; Istanbul and Rize Renault Dealership; Istanbul,Rize and Artvin Renault Dealership. Additionally, by SPM Automotive, spare parts’ wholesale, exportation, and importation are made in several countries such as England, Romania, Ukraine, Russia, China etc. With almost 500 employees and more than 5 million clients, Atılgan Group aims to create the brand which makes possible to client’s loyalty and to develop locally with global collaboration.
- Measuring Job Satisfaction in Atilgan Automotive
For our case study, a questionnaire was prepared. First of all, the literature review stage was completed and the Minnesota method was selected. Some questions were prepared for some of the factors, which are mentioned in previous paragraphs. Then, the questionnaire carried to the human resources manager of the company and feedback was got from him for editing the questionnaire. Then, questionnaires were distributed to employees to be applied.
For our survey, 50 employees were chosen randomly, from a different department. To choose employees to give a questionnaire, their position and jobs were considered. We divided them into two groups: clerical workers, technical workers. In the questionnaire, there are 14 main topics, most of the organizational variables which are given in the literature review. To clarify the topics, four or five questions were asked for each. We use a scale which is from 1 to 5. 1 shows fully dissatisfied, 5 shows fully satisfied. The questionnaires were anonymous; otherwise, employees may avoid making critics. After all of them gathered, data were analyzed with computer and results were illustrated with graphs.
- Results
After analyzes, we got some result. The results will be explained by giving the graphs.
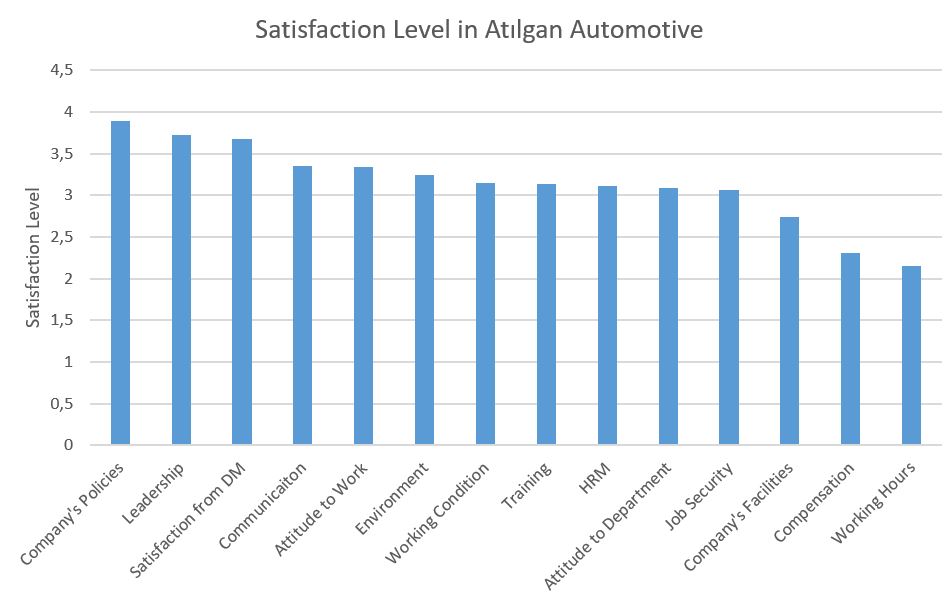
Figure 1: Satisfaction Level in Atılgan Automotive Inc.
The graph illustrates the employees’ satisfaction level for each factor. Such as company policies, leadership, communication factors are mostly satisfied factors for employees. However, job security, company’s facilities, compensation, working hours are most dissatisfied factors. These results can be interpreted according to the Two-Factor Theory. According to theory, there are two factors: Motivator and Hygiene Factors. Motivators are arising from intrinsic conditions of the job itself, such as recognition, achievement. Hygiene factors are extrinsic to the work itself like compensation. Hence, the graph can be interpreted with these theories, motivators are high but hygiene factors are not satisfied for employees.
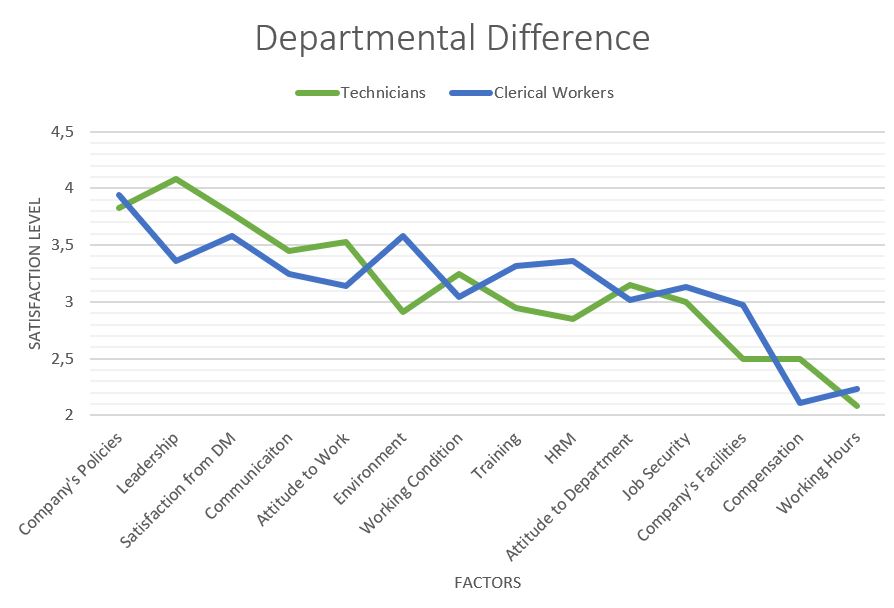
Figure 2: Departmental Difference in Job Satisfaction
General trends are similar to Figure 2, but this graph shows the departmental difference in the company. The green line presents the technicians who work in the car care service. The blue line presents managerial positions and clerical workers. For motivator factors, technicians are more satisfied than clerical workers, however, for hygiene factors, they are less satisfied. So the satisfaction level between hygiene factors and motivators are more balanced for clerical workers.
CONCLUSION
To conclude, to measure job satisfaction there are basically two methods. To apply what we learned from our literature search, we chose Minnesota Questionnaire which is the most common way to measure job satisfaction and applied it on a company, which is Atılgan Automotive. Then analyzes were done and shared with the company’s human resource manager. This kind of survey is very beneficial for a company. Surveys give management an indication of general levels of satisfaction, it increases the communication and productivity and effectiveness of the organization. Additionally, it is an opportunity to assess training needs.
References:
Alaam S., Sameena R., & Puja A. (2012). Identification of Variables Affecting Employee Satisfaction Their Impact on the Organization. Volume 5, pg. 34-36.
Diaz-Serrano, L. & Cabral A., (2005). Low pay, higher pay and job satisfaction within the European Union: Empirical evidence from fourteen countries. Institute for the Study of Labour, pg. 2.
Freeman, Shelly, (2005). Employee satisfaction: The key to a successful company. Retrieved on March 2011.
Hulin, C. L., & Judge, T. A. (2003). Job attitUdes. In W. C. Borman, D. R. ligen, & R. J.
Klimoski (Eds.), Handbook of psychology: Industrial and organizational psychology (pg. 255-276).
Locke, E.A. & Lathan, G.P. (1990). Theory of goal setting and task performance. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall, pg. 248-250.
Mitchell, T.R. & Lason, J.R. (1987). People in organization. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Moorman, R.H. (1993). “The influence of cognitive and affective based job satisfaction measures on the relationship between satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior”. Human Relations 6, pg. 759–776
Spector, P.E. (1997). Job satisfaction: Application, assessment, causes and consequences.
Thousand Oaks.